STCLOUD_mod4 cloud security FULL
20250707 STCLOUD Module 4 AWS Cloud Security FULL
This note has not been edited yet.
Announcements
- LE2 moved to week 12 instead of week 11
Module 4 AWS Cloud Security
(6:39)
- 2 entities that participate in the use of cloud: cloud provider (provide services and hardware), and client/renters/subscribers
- when you use cloud → you're a renter/subscriber
- you use resources from the provider
- SO... who's responsible for implementing security features? Who takes the blame if a security incident happens?
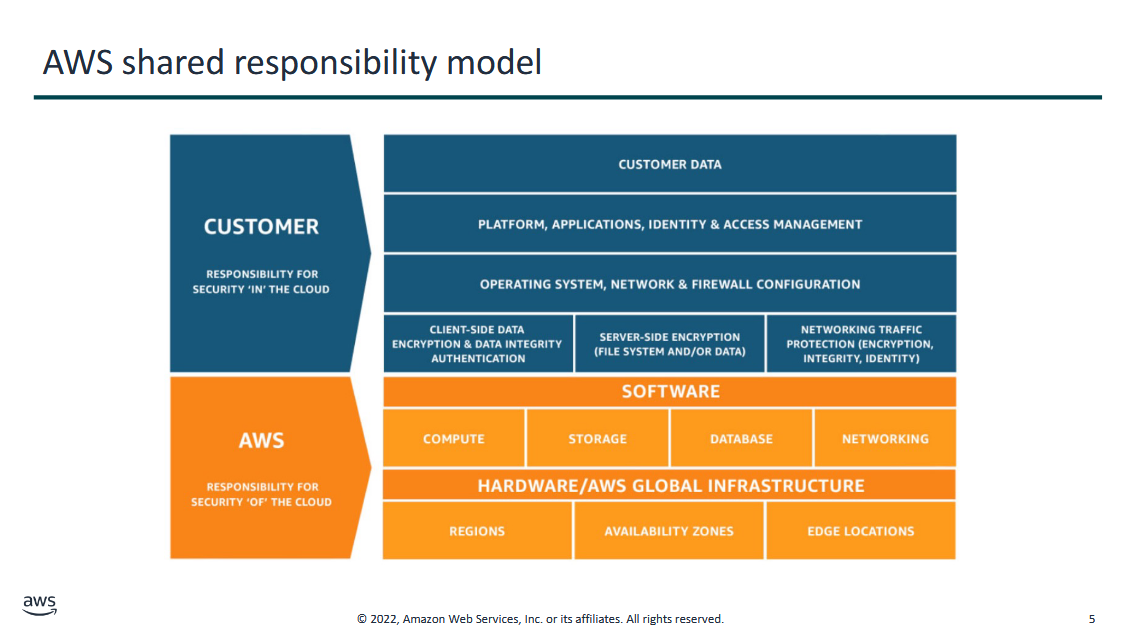
Section 1: Shared Responsibility Model
- in security, there's the concept of shared responsibility
- the responsibility of security does not fall on one entity, but it is shared between the customer and the cloud provider
ex. bike rental scenario:

- if you fell on the bike, the reason will dictate who's at fault
- you need the entire picture, the reason
- if you suck at biking, it's your fault
- if your bike is faulty, it's the provider's fault
- they go hand-in-hand: no matter how good you are at biking, if the bike is faulty then the provider is at fault.
as a customer, we have certain permissions we can perform:
- Customer Data: in GDrive, the one who manages the data within the GDrive is the customer → files, videos, photos, etc.
- Platform, Applications, Identity & Access Management: think of this as user permissions (sharing option) in GDrive that you activate on the drive
- Operating System, Network, & Firewall Configuration: if you're using an IaaS solution... if you're creating a VM, you're given full flexibility over the operating system including the network and firewall configurations
- Client-side Data, Encryption & Data Integrity, Authentication
- Server-side encryption, file system, and/or data
- encrypting files in the cloud may consume more space and time for processing
- Networking Traffic Protection (Encryption, Integrity, and Identity): includes your encryption
So user's responsibility includes:
- configuration is under the jurisdiction of the customer
- data
(from the ppt)
- the customer is responsible for the encryption of data at rest and data in transit. they should also ensure that the network is configured for security and that the security credentials and logins are managed safely
- the customer is responsible for the configuration of security groups and the configuration of the operating system that runs on compute instances that they launch (including updates and security patches)
Customers are responsible for security IN the cloud
Providers are responsible for security OF the cloud
as a cloud provider, they have control over the following:
- Software
- Compute, Storage, Database, Networking
- the cloud provider is responsible for protecting the infrastructure that runs all the services that are offered in the AWS cloud
- Hardware/AWS Global Infrastructure
- Regions, Availability Zones, Edge Locations
So the provider's responsibility includes:
- infrastructure
- services
- bc they are securing the cloud service
ex.
if you set the permissions in GDrive to only be accessible to you but someone unauthorized was able to get a hold of it because of a vulnerability in GDrive, then the fault is on the provider.\
the more control you have the more responsibility that you have as well
AWS Responsibility: Security OF the cloud
(24:49)
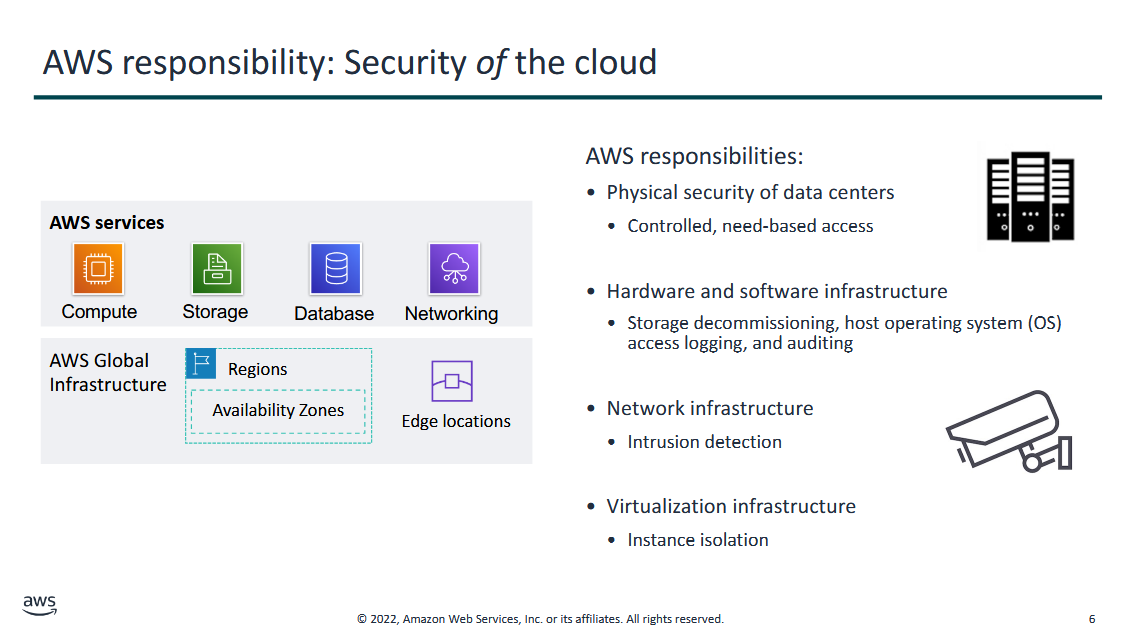
- services they provide and infrastructure they present
cloud providers are responsible for:
- physical security of data centers → only they know where their servers are held
- it is controlled, need-based access (access is restricted unless you really need)
- hardware and software infrastructure
- storage decommissioning, host operating system (OS), access logging, auditing
- storage decommissioning: sometimes cloud providers physically destroy the hard drives → "deleting" something just deletes a column in the file header, but the data is still there technically
- network infrastructure
- intrusion detection → they look at the network packets and they try to find patterns or any anomalies that a hacker would be trying to do, investigate vulnerabilities
- virtualization infrastructure
- instance isolation → makes sure that the instances are isolated from each one
Customer Responsibility: Security IN the cloud
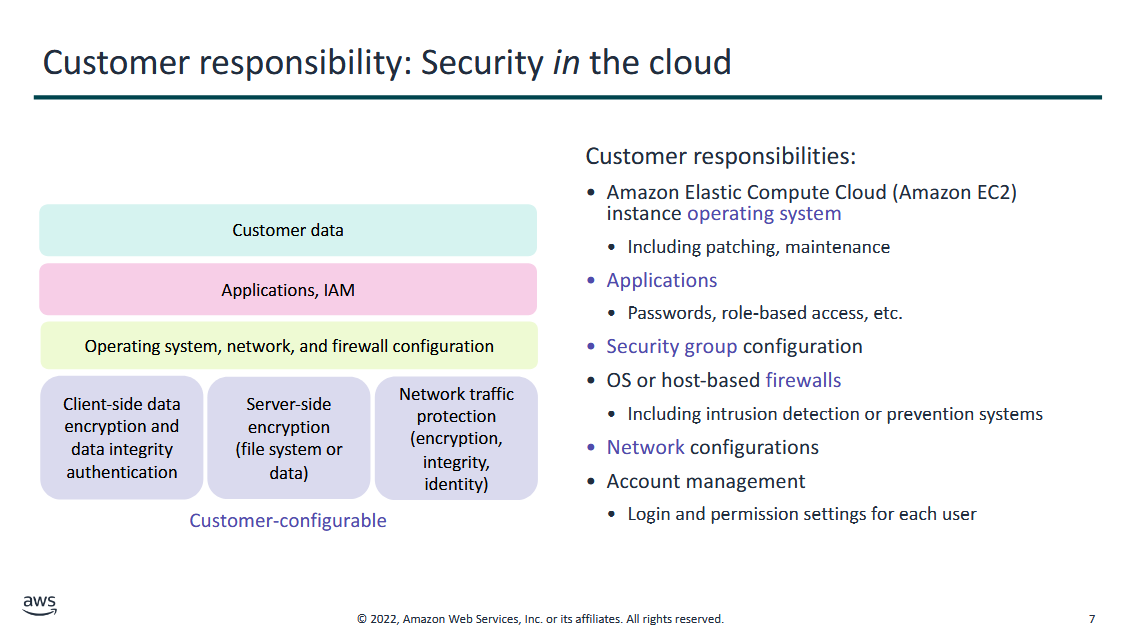
-
involves either data or configurations that are customer-configurable
-
highly dependent on the service model (IaaS, PaaS)
-
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance operating system
- including patching, maintenance
- EC2 is just a virtual machine → you select the instance type and size and the OS you like, it gets deployed automatically, but everything you do within that VM and the OS, patching, and maintenance are your responsibility
- anything OS and above is your responsibility
-
Applications
- passwords, role-based access, etc.
- if you have files shared to everyone or certain people, that's your responsiblity
-
Security Group configuration (Firewall)
-
OS or host-based firewalls (Firewall)
- including intrusion detection or prevention systems
- includes setting up your IPS
-
network configurations
- setting public/private networks, VPNs, subnets, etc. (for IaaS)
-
account management
- login and permission settings for each user
Service Characteristics and Security Responsibility
(34:38)
- there is a grey area in between because there are different levels of responsibility depending on the Service Model
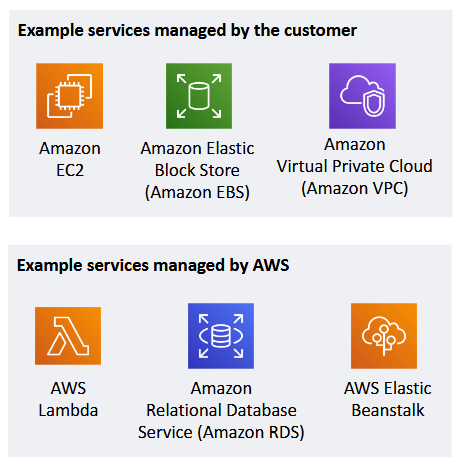

Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- most control over the resources → VMs, compute, containers, storage, network
- customer has more flexibility over configuring networking and storage settings
- customer is responsible for managing more aspects of the security
- customer configures the access controls
- Amazon EC2 (virtual machines)
- Amazon Block Store (block storage)
- Amazon VPC (networks)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- balance of both/has some control → apps of choice, version, programming language (can't choose OS and below)
- customer does not need to manage the underlying infrastructure
- AWS handles the operating system, database patching, firewall configuration, and disaster recovery
- customer can focus on managing code or data
- AWS Lambda (serverless compute → you have a server but you don't manage the server)
- ex. you have a web application that runs a python script on images of food. the image gets sent to a server you dont manage, output is the amount of calories based on the image
- cheapest option for compute, all you have to do is do API calls to the python code and you get the result
- Amazon RDS ("managed database" → the server is managed by the provider na you just need to choose what kind of DB, focus on your data)
- Amazon Elastic Beanstalk (orchestration → deploys the machine and servers that you like, you just need to set the configurations)
Gemini on orchestration: In the context of cloud computing and cloud services, orchestration refers to the automated arrangement, coordination, and management of complex services, workflows, and resources across various cloud environments. Cloud orchestration is about bringing order and automation to the complexity of modern cloud environments, allowing organizations to manage their cloud resources and services with greater efficiency, agility, and control.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- least control over the resources, we are just a user/subscriber
- software is centrally hosted
- licensed on a subscription model or pay-as-you-go basis
- services are typically accessed via web browser, mobile app, or application programming interface (API)
- customers do not need to manage the infrastructure that supports the service
think of GDrive..
provider handles:
- Server for the application and files
- GDrive app itself
- Drive version
- Storage
User: data and permissions
- AWS Trusted Advisor
- AWS Shield
- Amazon Chime
questions: (47:13-1:07:26)
- in security: principle of least privilege → the cloud and you should give the user the least amount of privilege to do something, but enough that they can do their job
- because more privilege → more vulnerabilities → cloud handles this by not giving access to something, everything is denied by default, so you have to be the one to configure something and give someone else access
Section 2: AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
-
same thing as lab activity # 1
-
IAM is basically some directory services, similar to DLSU Active Directory
-
use IAM to manage access to AWS resources
- a resource is an entity in an AWS account that you can work with
- ex: an Amazon EC2 instance or an Amazon S3 bucket
-
Example: Control who can terminate Amazon EC2 instances
-
define fine-grained access rights
- WHO can access the resources
- WHICH resources can be accessed and WHAT can the user do to it
- HOW resources can be accessed
-
IAM is a no-cost AWS account feature
involves the following entities/essential components:
- USER: a person or an application (via keys used to access stuff) that can authenticate with an AWS account
- GROUP: a collection of IAM users that are granted identical authorization, like departments, colleges, batches, organizations etc.
- POLICY: the document that defines which resources can be accessed and the level of access to each resource, literally this is just the permission/s
- a policy can be assigned to a role, group, or user
- ROLE: useful mechanism to grant a set of permissions for making AWS service requests
- keyword: temporary, this is a temporary set of permissions
- right now you're a student, your role changes from student to alumni when you graduate. and that affects what you can do
Authorization: What actions are permitted
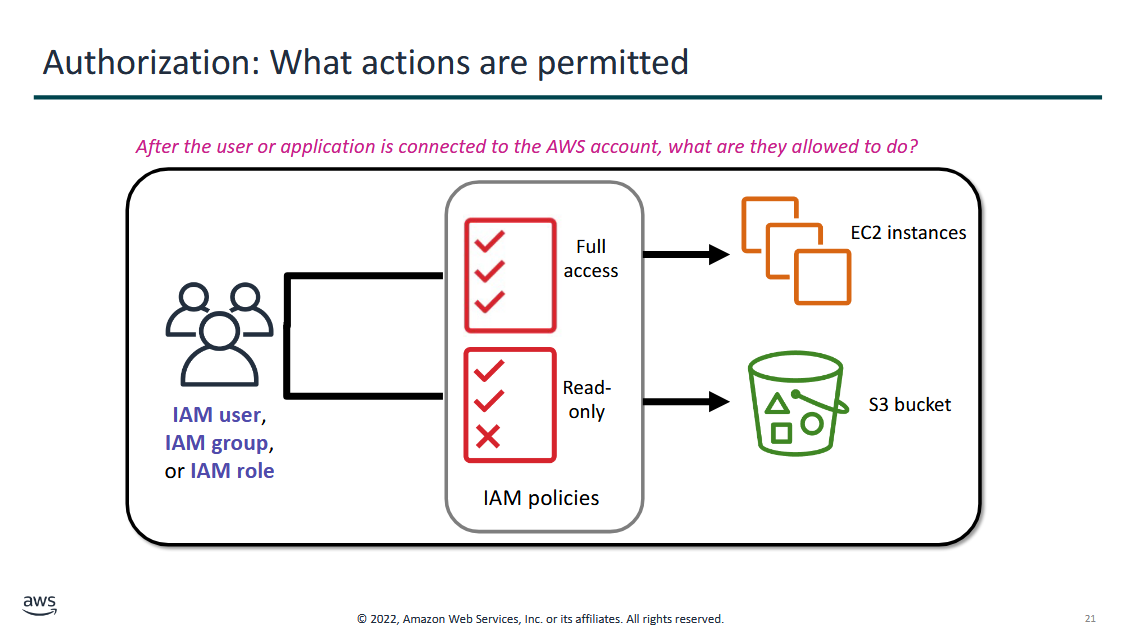
- tells you what you can do on a resources
- tells you what you cannot do on a resource
- policies or permissions are granted on users, groups, or roles on selection
IAM: Authorization (best practices)
- assign permissions by creating an IAM policy
- permissions determine which resources and operations are allowed
- all permissions are implicitly denied by default
- if something is explicitly denied, it is never allowed
- best practice: follow the principle of least privilege → give the user the least amount of access to do something, but enough for them to do their job
- the scope of IAM service configurations is global. Settings apply across all AWS regions
- another good practice is to utilize groups over individual users, then just add the users to the group
IAM: Policy Example
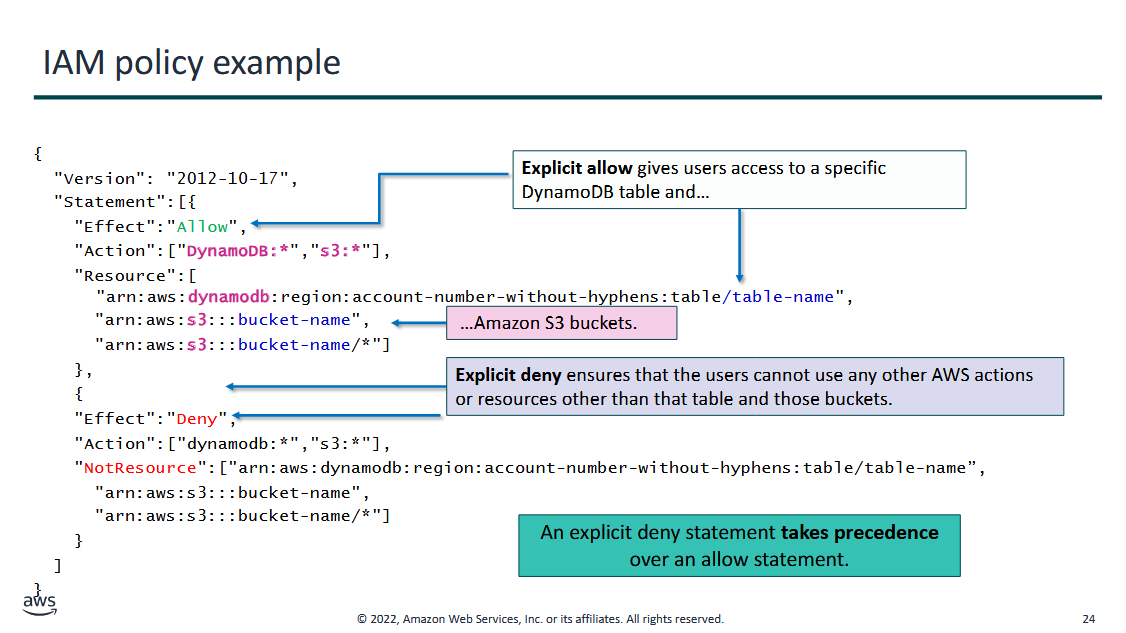
- Effect: if you can/cannot do it (allow/deny)
- Action: what API call can you do (AWS management console is all API calls)
- Resource: which one in the cloud are you referring to?
IAM: Permissions
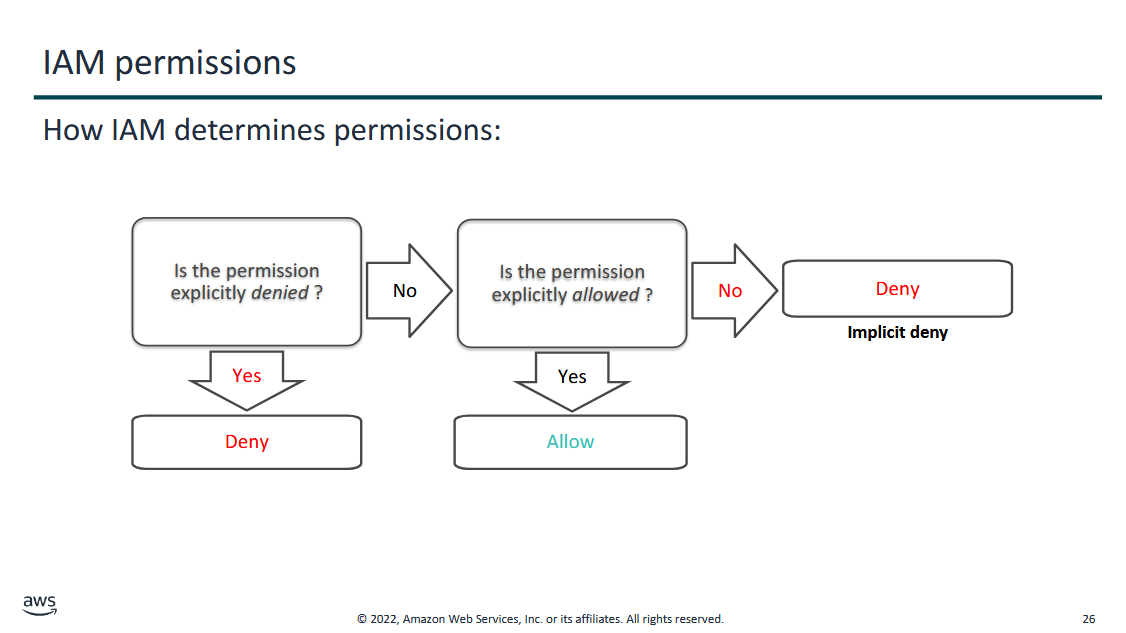
- conditional statement flowchart
- if explicitly denied → denied si user
- if there's no deny statement but allow statement → allow
- if there's no deny, no allow statement → deny
Section 3: Securing a new AWS Account, best practices when using the cloud
AWS account root user access versus IAM access
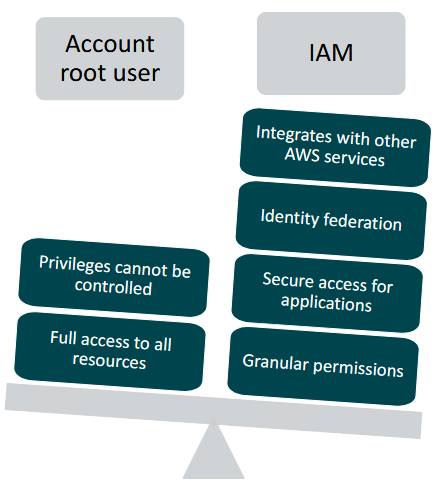
- best practice: do not use the AWS account root user except when necessary
- access to the account root user requires logging in with the email address and password that you used to create the account
- root user is a super admin
- IAM Access → the user inside the account based on the policies in the directory services
- ex. DLSU is the super admin, the individual students and faculty are accounts
- example actions that can be done with the account user
- update the account root user pw
- change the AWS support plan
- restore an IAM user's permissions
- change account settings (contact info, allowed regions, etc.)
Securing a new AWS account: Account root user, MFA, AWS CloudTrail, Billing Reports
step 1: stop using the account root user as soon as possible
- the account root user has unrestricted access to all your resources
to stop using the account root user
- while you are logged in as the account root user, create an IAM user for yourself. save the access keys if needed
- create an IAM group, give it full admin perms, and then add the IAM user to the group
- disable and remove your account root user access keys if they exist
- enable a password policy for users
- sign it with your new IAM user credentials
- store your account root user credentials in a secure place
step 2: enable multi-factor authentication
- require MFA for your account root user and for all IAM users
- you can also use MFA to control access to AWS service APIs
options for retrieving the MFA token
- virtual MFA-compliant applications (Google authenticator, Authy)
- U2F security key devices (Yubikey)
- hardware MFA options (Key fob or display card from Gemalto)
step 3: use AWS CloudTrail (logs)
- CloudTrail tracks user activity on your account
- logs all API requests to resources in all supported services in your account
- basic AWS CloudTrail event history is enabled by default, and is free
- contains all management event data on latest 90 days of account activity
to access CloudTrail:
- log into AWS management console and choose CloudTrail service
- click event history to view/filter/search past 90 days
- to enable logs beyond 90 days and enable specific event altering, create a trail:
- from CloudTrail Console trails page, click create trail
- give it a name, apply to all regions, and create a new Amazon S3 bucket for log storage
- configure access restrictions on the S3 bucket (ex. only admins can have access)
step 4: enable a billing report, such as the AWS Cost and Usage Report
- billing reports provide information about your use of AWS resources and estimated costs for that use (just logs but for costs)
- AWS delivers the reports to an Amazon S3 bucket that you specify
- report is updated at least once a day
- the AWS Cost and Usage Report tracks your AWS usage and provides estimated charges associated with your AWS account, either by the hour or by the day
Summary for best practices:
- user permissions: follow the principle of least privilege
- do not use the AWS account root user except when necessary
- enable multi-factor authentication
- use logs/AWS CloudTrail
- enable billing reports (logs but for the costs)
Section 4: Securing Accounts
(1:19:26)

- AWS Organizations (organizational management) enables you to consolidate multiple AWS account so that you centrally manage them
- IAM deals with users
- Organizations deals with accounts
- Security Features of AWS Organizations:
- Group AWS accounts into organizational units (OUs) and attach different access policies to each OU
- integration and support for IAM
- permissions granted to a user are the intersection of what is allowed by AWS organizations and what is granted by IAM in that account
- use service control policies to establish control over the AWS services and API actions that each AWS account can access
IAM → users
Organizations → Accounts
IAM policy → IAM users
SCPolicies → accounts (are not under IAM, you have to join them in an organization to use SCPs)
AWS Organizations: Service Control Policies
- Service Control Policies (SCPs) offer centralized control over accounts
- limit permissions that are available in an account that is part of an organization
- ensures that accounts comply with access control guidelines
- SCPs are similar to IAM permissions policies →
- use similar syntax
- an SCP never grants permissions tho
- SCPs specify the maximum permissions for an organization
AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS)

AWS KMS features:
- create and manage encryption keys
- enables you to control the use of encryption across AWS services and in your applications
- integrates with AWS CloudTrail to log all key usage
- uses hardware security modules (HSMs) that are validated by the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 140-2 to protect keys
Amazon Cognito (centralized log in and sign-in options)

- adds user sign-up, sign-in, and access control to your web and mobile applications
- scales to millions of users
- supports sign-in with social identity providers like FB, Google, Amazon, and enterprise identity providers like Microsoft Active Directory via Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 2.0
- because it's centralized → easier for users to manage accounts and remember their passwords
AWS Shield

- managed distributed denial of service (DDoS) protection service
- safeguards applications running on AWS
- provides always-on detection and automatic inline mitigations
- AWS Shield Standard enabled for at no additional cost
- AWS Shield Advanced is an optional paid service
- use it to minimize application downtime and latency
another best practice: use features to protect yourself readily available on the cloud or you can configure them yourself for added security, and to minimize downtime and latency
Section 5: Securing Data
types of data
- data in rest (storage)
- data in transit (network)
- data in processing (memory)
how do you secure your data? → encryption
Encryption of data at rest
- Encryption encodes data with a secret key, which makes it unreadable
- only those who have the secret key can decode the data
- if someone gets a hold of your files, they will not be able to understand
- AWS KMS can manage the secret keys
- AWS supports encryption of data at rest
- data at rest = data stored physically on disk or on tape
- you can encrypt data stored in any service that is supported by AWS KMS including S3, EBS, EFS, RDS
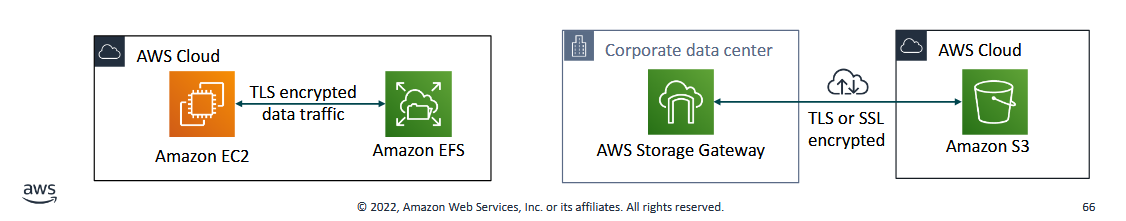
Encryption of data in transit
- encryption of data in transit (data moving across a network)
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) - formerly SSL - is an open standard protocol
- AWS Certificate Manager provides a way to manage, deploy, and renew TLS or SSL certificates
- secure HTTP/HTTPS creates a secure tunnel using TLS or SSL for the bidirectional exchange of data
- AWS services support data in transit encryption.
- so if someone is trying to sniff the traffic over the network like a man-in-the-middle attack, they wont be able to get the data
Section 6: Working to ensure Compliance
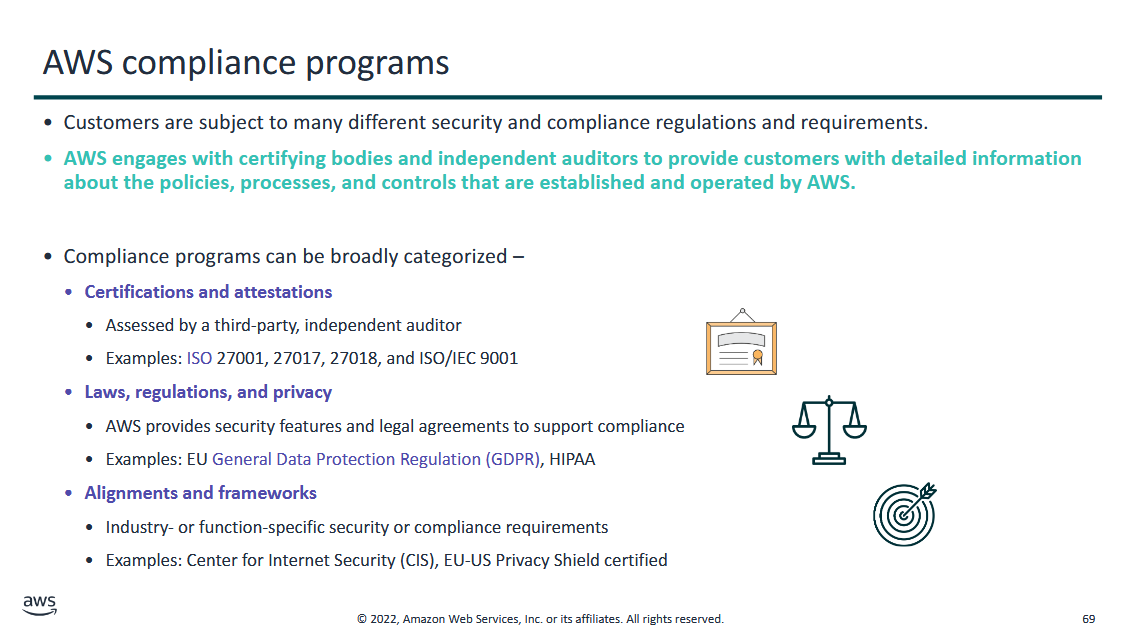
AWS engages with certifying bodies and independent auditors to provide customers with detailed information about the policies, processes, and controls that are established and operated by AWS.
- by putting your standards and data on the cloud, you have to follow certain standards, laws, and certifications
- just because you use cloud, doesn't mean you're certified. like if you're certified and your configuration in IaaS is bad, then it's your fault
- follow compliance programs so you can follow good practices, the cloud service provider will also guide you on these practices
- customize your functionalities to ensure your users are going to be secure and you're following secure practices